You can recover from some errors. Others, like system or network failures are fatal. But even in the fatal case, your Talend Open Studio job should die gracefully, notifying the operations team and leaving the data in a good state. This post presents three error handling strategies for your Talend jobs.
Some Talend Open Studio job errors are alternate paths that, though infrequent, occur often enough to justify special programming. This programming may come in the form of guard conditions, special logic applied to route the special case to another subjob. For an example of these type of errors, see this blog post on ETL Filter Patterns.
Other errors are related to system and network activity or are bugs. There are a few ways to handle this class of error in Talend Open Studio.
Do Nothing
For simple jobs, say an automated administrative task, you can rely on the exception throwing of Talend Open Studio. An example is a simple input to output job where a database failure in writing the output results in a system error. This is expressed in the Run View as a red stack trace.
Subjob or Component Error Triggers
Each subjob and component has a return code that can drive additional processing. The Subjob Ok/Error and Component Ok/Error can be used to steer the error toward an error handling routine like the tSendMail component. This example looks for a connection error (the database is off) or a file processing error (the database is on, but the table name is wrong).
Both an individual subjob and a finer-grain component can be tested. The screenshot shows two tSendMail routines being called from an OnSubjobError trigger.
While testing the individual subjobs and components has the advantage of providing error handling tied to the specific case, there are disadvantages in maintenance and testing. Maintenance suffers because the job becomes cluttered with extra components which can confuse the normal processing, less frequent processing, and the error handling. Testing is harder because there are more test cases.
Sometimes, there is a need for this level of detail. You may want to send a file that represents an intermediate stage of processing via email. This file isn't available throughout the job, and not every failure can handle this.
tAssertCatcher
A more general strategy is to define an error handling subjob to be performed when an error -- any error -- occurs. This has the important advantage of consolidating the error handling, dramatically reducing testing. It puts the burden of testing for error conditions on Talend (where it belongs).
To implement the general strategy, use the tAssertCatcher component which will be invoked whenever any component throws an error.
If there's a failure in the XSL component (tXSLT) or other component resulting in a Java exception, the job will continue with the error handler (in this case a tLogRow) attached to the tAssertCatcher. tAssertCatcher can route an error message to other handlers like a tSendmail.
Components like tXSLT don't need any additional configuration to use tAssertCatcher. ThetFileInputXML has a "Die on error" checkbox that needs to be set.
In the following screenshot, the database component tMSSqlOutput_1 has "Die on error" set. If the flag is not set, then the tMSSqlOutput will print a message and the tAssertCatcher will not be called. This particular example caught errors from the connection component (bad login) and the tMSSqlOutput component (DB-generated unique constraint violation and invalid insert of identity column).
Let Talend Work
Handling system errors is different than alternate paths and conditions that arise during coding a Talend job. Sometimes, you'll have a specific error routine for a specific system error condition. But where possible, let Talend throw the system errors and catch them with a tAssertCatcher.
Some Talend Open Studio job errors are alternate paths that, though infrequent, occur often enough to justify special programming. This programming may come in the form of guard conditions, special logic applied to route the special case to another subjob. For an example of these type of errors, see this blog post on ETL Filter Patterns.
Other errors are related to system and network activity or are bugs. There are a few ways to handle this class of error in Talend Open Studio.
Do Nothing
For simple jobs, say an automated administrative task, you can rely on the exception throwing of Talend Open Studio. An example is a simple input to output job where a database failure in writing the output results in a system error. This is expressed in the Run View as a red stack trace.
 |
| Simple Job with No Extra Error Handling Configured |
Each subjob and component has a return code that can drive additional processing. The Subjob Ok/Error and Component Ok/Error can be used to steer the error toward an error handling routine like the tSendMail component. This example looks for a connection error (the database is off) or a file processing error (the database is on, but the table name is wrong).
Both an individual subjob and a finer-grain component can be tested. The screenshot shows two tSendMail routines being called from an OnSubjobError trigger.
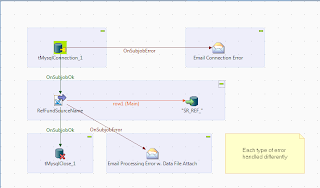 |
| Error Handling Tailored to the Subjob (or Component) |
Sometimes, there is a need for this level of detail. You may want to send a file that represents an intermediate stage of processing via email. This file isn't available throughout the job, and not every failure can handle this.
tAssertCatcher
A more general strategy is to define an error handling subjob to be performed when an error -- any error -- occurs. This has the important advantage of consolidating the error handling, dramatically reducing testing. It puts the burden of testing for error conditions on Talend (where it belongs).
To implement the general strategy, use the tAssertCatcher component which will be invoked whenever any component throws an error.
 |
| A Shared Error Handler with tAssertCatcher |
 |
| tAssertCatcher Config |
In the following screenshot, the database component tMSSqlOutput_1 has "Die on error" set. If the flag is not set, then the tMSSqlOutput will print a message and the tAssertCatcher will not be called. This particular example caught errors from the connection component (bad login) and the tMSSqlOutput component (DB-generated unique constraint violation and invalid insert of identity column).
 |
| An Example with Database Components |
Let Talend Work
Handling system errors is different than alternate paths and conditions that arise during coding a Talend job. Sometimes, you'll have a specific error routine for a specific system error condition. But where possible, let Talend throw the system errors and catch them with a tAssertCatcher.
Copycat from http://bekwam.blogspot.fr/2011/04/three-error-handling-strategies-in.html !!
ReplyDelete